Understanding Real Estate Investment Trusts
May 20, 2024 By Triston Martin
You can invest in real estate by using a type of company called a real estate investment trust (REIT). REITs let many people put their money together to buy big-money, income-making real estate. This includes different types of properties such as commercial, residential, and industrial real estate. These pieces of writing will tell you what REITs are and how they work, also showing the ways to invest money in them.
What is a REIT?
A real estate investment trust (REIT) is like a mutual fund. It's a company that owns, manages, or provides financing for income-producing real estate. This type of setup lets people who are not big players in the industry, known as individual investors, have an opportunity to earn part of the money produced by owning commercial property without needing to purchase and handle any properties on their own or finance them. REITs have to give out a minimum of 90% of their taxable earnings as payouts to shareholders which usually makes these trusts liked by investors looking for steady money coming in source.
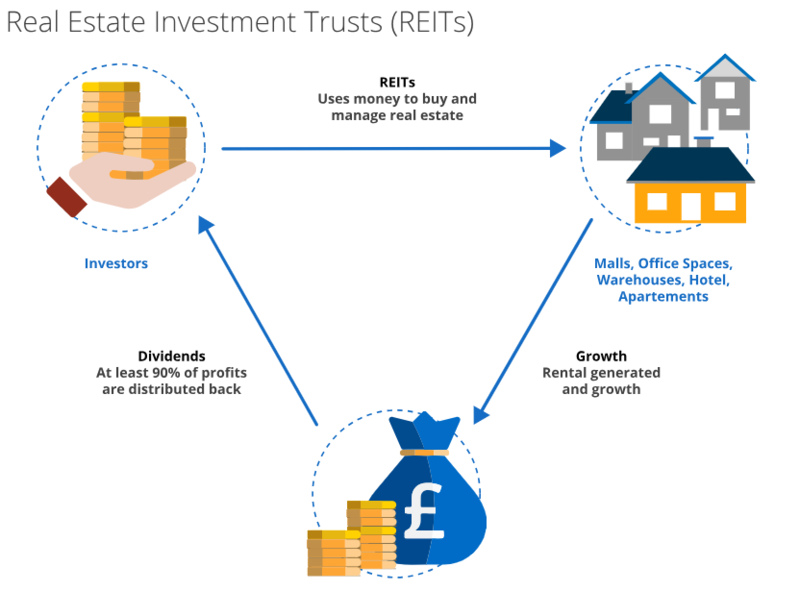
The reason behind the creation of REITs by Congress in 1960 was to let individual investors share in the income produced from big, varied real estate portfolios. They provide a simple method for people to invest their money into property without having to manage or finance it themselves. Individuals can buy shares of REITs on stock exchanges which makes them more fluid investments compared with direct real estate ownership. This arrangement gives tax benefits too because REITs aren't subjected to paying corporate taxes on profits that are shared as dividends.
- Historical Context: Established by Congress in 1960 to democratize real estate investment.
- Tax Advantages: REITs avoid corporate taxes by distributing 90% of taxable income to shareholders.
Types of REITs
REITs can be classified into multiple kinds, which concentrate on various areas within the real estate market. Equity REITs possess and handle real estate properties, gaining income via the lease of space and collection of rents. Mortgage REITs (mREITs) finance income-generating real estate by buying or creating mortgages and mortgage-backed securities, gaining money from interest on these financial instruments. Hybrid REITs use a mixed method, combining the investment tactics of both equity REITs and mortgage REITs. These organizations put money into properties as well as mortgages.
Equity REITs might specialize even more, breaking down into sub-sectors like retail, office, residential, healthcare, or industrial property groups. Every one of these has its unique risk and return features that rely on the demand from market conditions as well as the economy and trends specific to the sector. For example, healthcare REITs put their money into hospitals, nursing homes, and medical offices which benefit from a growing older population along with rising demand for healthcare services. At the same time, those REITs that are dedicated to industrial properties, like warehouses and logistics centers, benefit from the increasing popularity of online shopping.
- Sub-sector Specialization: Equity REITs can target specific property types like healthcare or industrial.
- Market Dynamics: Performance varies based on economic conditions and sector-specific trends.
How REITs Work?
Real Estate Investment Trusts, also known as REITs, function by gathering the money of many investors to buy and handle a varied collection of real estate assets. The income made from these properties - it can be rent payments, lease contracts, or even mortgage interest - is then shared with the shareholders in the form of dividends. For a business to be considered a REIT, it has to follow certain rules set by law. This includes distributing a minimum of 90% of its taxable earnings each year and investing at least 75% of total assets into real estate.
Apart from rules set by regulators, REITs also gain advantages from economies of scale, professional management, and availability in capital markets. These factors help to improve the way properties are managed and acquired by making use of property-related knowledge that can be used to select what is best for investors. They often hire real estate professionals with experience who can make knowledgeable choices about purchasing, developing, or leasing property. This skill aids in getting the most out of investments for investors while managing dangers linked with owning and running properties.
- Economies of Scale: Large-scale operations lead to more efficient management and acquisition strategies.
- Professional Management: Expert real estate professionals handle investment decisions, maximizing returns.
Benefits of Investing in REITs
REITs bring many benefits. They offer a liquid way to invest in real estate because shares of REITs that are traded publicly can be bought and sold on big stock exchanges. REITs provide diversification because they usually invest in different property types across various areas. Furthermore, normal dividend disbursements can offer a stable flow of income to investors. This characteristic makes REITs more appealing to those who are concentrating on investments that generate regular earnings.
A big advantage of REITs is the chance for capital appreciation. When the value of properties being used by REITs goes up, so does the worth of their shares. This can provide the possibility for growth over time. Also, REITs might work as a protection against inflation because usually property values and rents go up during times of inflation. This can help maintain the purchasing power of the income generated by REITs.
- Capital Appreciation: Potential for long-term growth as property values increase.
- Inflation Hedge: Property values and rents typically rise with inflation, preserving income value.
Risks Associated with REITs
Though REITs make a great part of investment collection, they do come with some risks. The market changes can make the value of REIT shares go up or down, and how well the real estate does also affects how much you get back on your investment. Changes in interest rates might influence mortgage REITs' profitability; when rates are higher it could lead to greater borrowing expenses and smaller profit margins for them as well. Before investing in REITs, investors must perform comprehensive research and assess their risk capacity.
REIT performance can be greatly influenced by economic decline, leading to a possible increase in vacancy rates and a decrease in rental income. Additionally, certain property sectors may encounter distinct problems; for example, retail REITs might experience difficulties due to the change towards digital shopping while office REITs could face impacts from alterations in workplace tendencies like remote working becoming more common. Changes in regulations and the cycles of property markets pose probable risks to investments made in REITs too.
- Economic Downturns: Vacancy rates may rise, and rental income may decline during economic recessions.
- Sector-Specific Challenges: Retail and office REITs may face unique difficulties due to market trends.
Investment Strategies for REITs
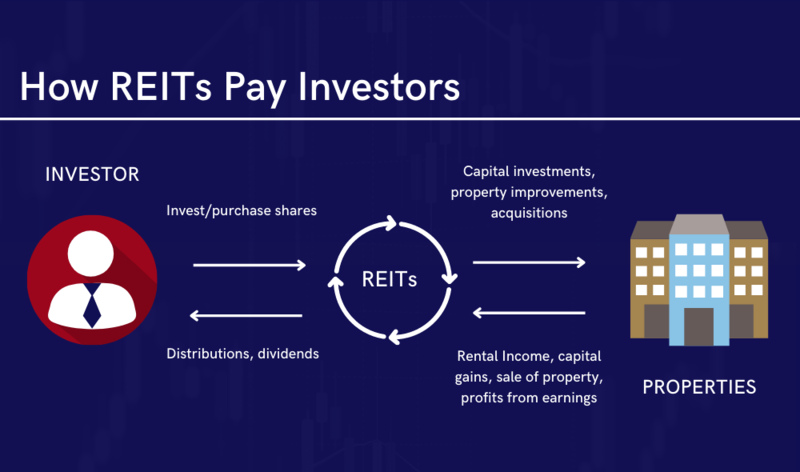
When you think about investing in REITs, there are some strategies to remember. One method is concentrating on particular sectors of the real estate market that might have more growth chances or steadiness, like healthcare or industrial properties. Spreading your investment across various kinds of REITs, such as equity and mortgage REITs can also assist in balancing risk. Moreover, investors might decide to put their money in REIT mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). These options give them access to many different REITs at once and can make the investing procedure easier.
People who invest for long periods could search for REITs that possess powerful management teams and a history of good performance. Examining the real estate property groupings underneath and comprehending the market factors impacting them might help in creating more knowledgeable investment choices. For people looking to make an income, it could be beneficial to concentrate on REITs that regularly pay out high dividends. The tax effect and how REITs fit in with the diversification of risks for the investment portfolio is also an important aspect to think about.
- Management Quality: Look for REITs with experienced management and strong performance records.
- Dividend Yield: Focus on REITs with consistent and high dividend payments for steady income.
Conclusion
One key benefit of REITs is that they allow regular people to invest in real estate without having to handle the management tasks associated with owning properties. If you comprehend what REITs are, how they function, and the different investment techniques involved, you can make educated choices and possibly improve your portfolio's performance by including exposure to real estate. Just like any other kind of investment, it's very important to think about all possible risks and do deep research before investing in REITs. This is necessary for making sure that this type of investment matches your overall financial goals and ability to accept riskiness.








